|
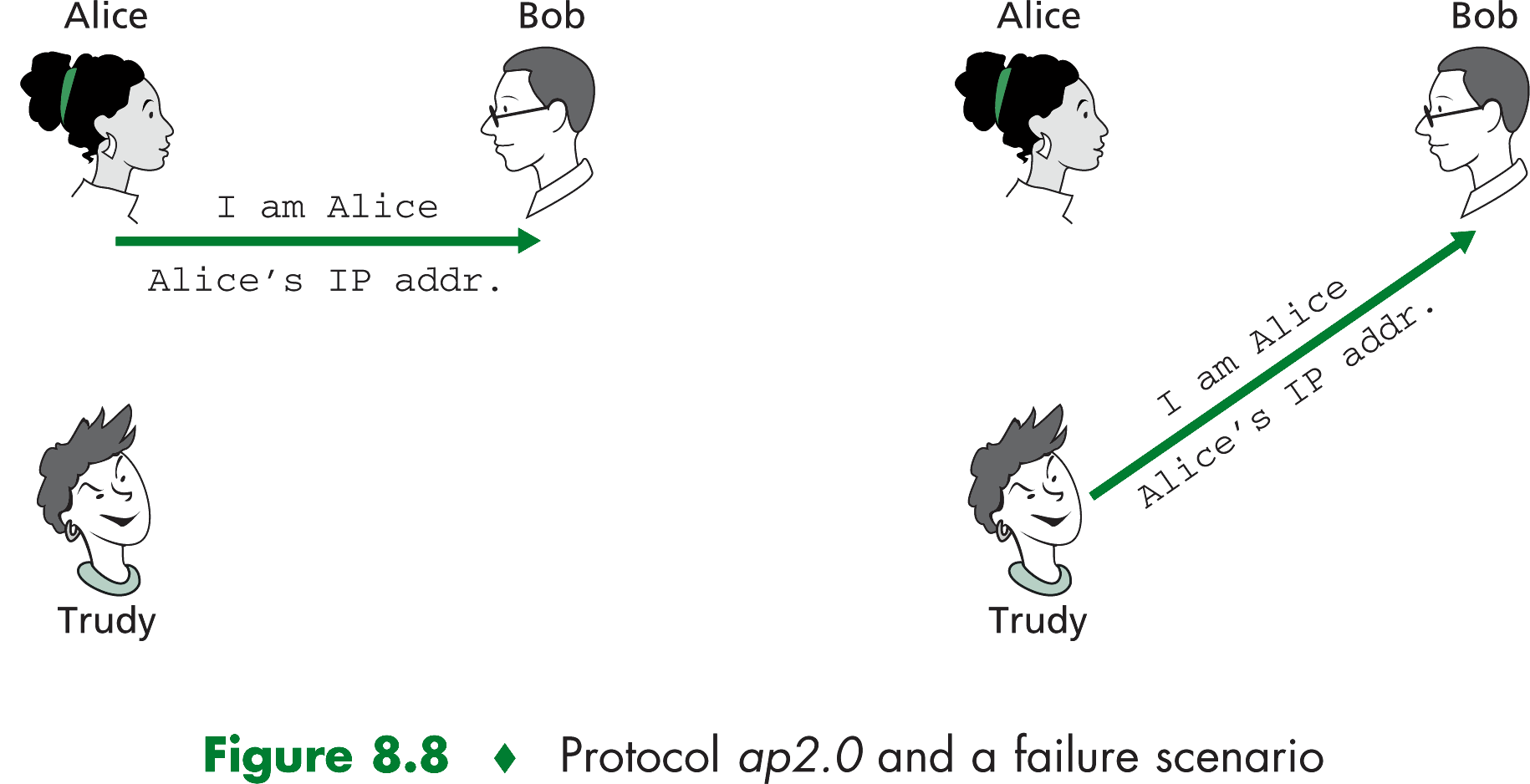
From our study of the network and data link layers, we know that it is not that hard to create an IP datagram, put whatever
IP source address we want into the IP datagram, and send the datagram over the link-layer protocol to the first-hop router.
From then on, the incorrectly source-addressed datagram would be dutifully forwarded. This approach is a form of IP
spoofing, a well-known security attack. IP spoofing can be avoided if your first-hop router is configured to forward
only datagrams containing your IP source address. This capability is not universally deployed or enforced.
|
